The publication by our former MSc student Sadroddin Alavipanah has been published. The article “The Role of Vegetation in Mitigating Urban Land Surface Temperatures: A Case Study of Munich, Germany during the Warm Season” is the result of his MSc thesis within the Global Change Ecology study program.
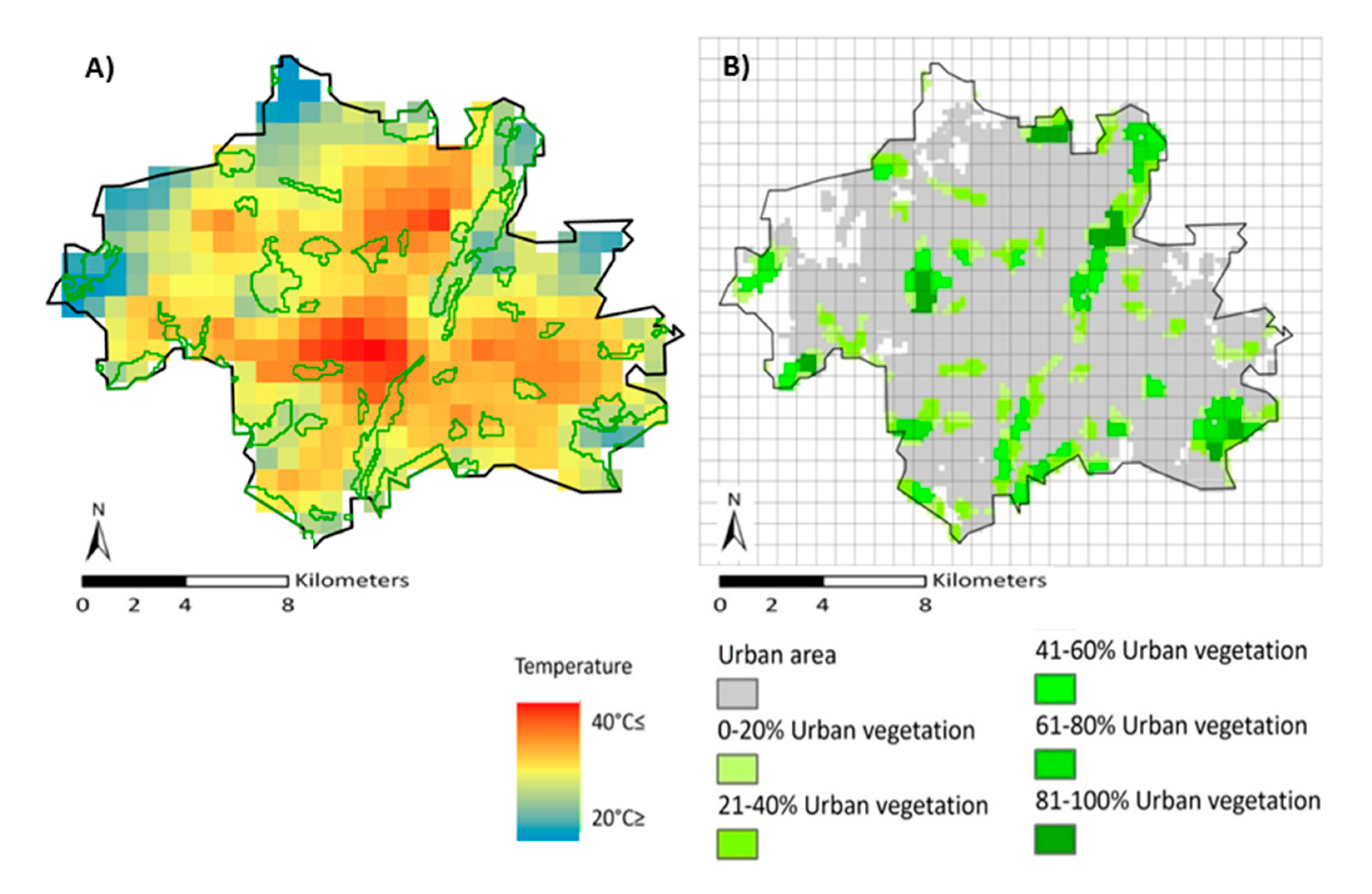 abstract: The Urban Heat Island (UHI) is the phenomenon of altered increased temperatures in urban areas compared to their rural surroundings. UHIs grow and intensify under extreme hot periods, such as during heat waves, which can affect human health and also increase the demand for energy for cooling. This study applies remote sensing and land use/land cover (LULC) data to assess the cooling effect of varying urban vegetation cover, especially during extreme warm periods, in the city of Munich, Germany. To compute the relationship between Land Surface Temperature (LST) and Land Use Land Cover (LULC), MODIS eight-day interval LST data for the months of June, July and August from 2002 to 2012 and the Corine Land Cover (CLC) database were used. Due to similarities in the behavior of surface temperature of different CLCs, some classes were reclassified and combined to form two major, rather simplified, homogenized classes: one of built-up area and one of urban vegetation. The homogenized map was merged with the MODIS eight-day interval LST data to compute the relationship between them. The results revealed that (i) the cooling effect accrued from urban vegetation tended to be non-linear; and (ii) a remarkable and stronger cooling effect in terms of LST was identified in regions where the proportion of vegetation cover was between seventy and almost eighty percent per square kilometer. The results also demonstrated that LST within urban vegetation was affected by the temperature of the surrounding built-up and that during the well-known European 2003 heat wave, suburb areas were cooler from the core of the urbanized region. This study concluded that the optimum green space for obtaining the lowest temperature is a non-linear trend. This could support urban planning strategies to facilitate appropriate applications to mitigate heat-stress in urban area.
abstract: The Urban Heat Island (UHI) is the phenomenon of altered increased temperatures in urban areas compared to their rural surroundings. UHIs grow and intensify under extreme hot periods, such as during heat waves, which can affect human health and also increase the demand for energy for cooling. This study applies remote sensing and land use/land cover (LULC) data to assess the cooling effect of varying urban vegetation cover, especially during extreme warm periods, in the city of Munich, Germany. To compute the relationship between Land Surface Temperature (LST) and Land Use Land Cover (LULC), MODIS eight-day interval LST data for the months of June, July and August from 2002 to 2012 and the Corine Land Cover (CLC) database were used. Due to similarities in the behavior of surface temperature of different CLCs, some classes were reclassified and combined to form two major, rather simplified, homogenized classes: one of built-up area and one of urban vegetation. The homogenized map was merged with the MODIS eight-day interval LST data to compute the relationship between them. The results revealed that (i) the cooling effect accrued from urban vegetation tended to be non-linear; and (ii) a remarkable and stronger cooling effect in terms of LST was identified in regions where the proportion of vegetation cover was between seventy and almost eighty percent per square kilometer. The results also demonstrated that LST within urban vegetation was affected by the temperature of the surrounding built-up and that during the well-known European 2003 heat wave, suburb areas were cooler from the core of the urbanized region. This study concluded that the optimum green space for obtaining the lowest temperature is a non-linear trend. This could support urban planning strategies to facilitate appropriate applications to mitigate heat-stress in urban area.
Alavipanah, S.; Wegmann, M.; Qureshi, S.; Weng, Q.; Koellner, T. The Role of Vegetation in Mitigating Urban Land Surface Temperatures: A Case Study of Munich, Germany during the Warm Season. Sustainability 2015, 7, 4689-4706.








